等离子体谐振器(DGTD)
此示例使用间断伽辽金时域(DGTD)方法对一种表现出类法诺共振的等离子体结构进行建模和分析。它展示了如何计算消光光谱,如何识别各个共振频率和品质因数,以及如何获取各个模式的场分布。
等离子体谐振器能够在纳米尺度上限制并强烈增强电磁场。此外,通过设计同时具有辐射(亮)模式和非辐射(暗)模式的结构,可以实现类似范诺共振的特性,其特点是具有相对尖锐且可能不对称的光谱特征。
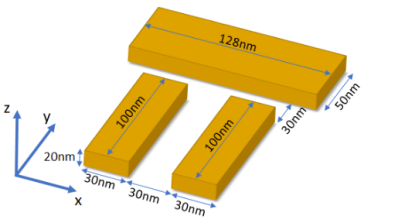
下面展示的“石棚”结构就是一个这样的谐振器的例子。它由三根金棒组成。材料参数和确切尺寸取自参考文献[1],如下所示。在简化的图景中,我们可以将顶部的棒视为偶极子,它能很好地与沿 x 轴极化的平面波耦合(亮模式)。底部的一对垂直棒可以视为电四极子,它与平面波耦合较差(暗模式)。亮模式与暗模式的耦合以及由此产生的干涉导致了其特有的光谱特征。
Run and results
Step 1:
Plane-wave excitation and cross section calculation
Open the simulation file and the script “dgtd_dolmen_cross_sections.lsf”. The script configures the project to compute the cross sections of the Dolmen structure, runs the simulation and plots the results.
The script enables a plane wave source with propagation direction along the z-axis and with polarization
which corresponds to a polarization angle of approximately 26.5 degrees. This angle is chosen to break any obvious symmetry and to allow coupling to all modes. The plane wave is injected using a rectangular total-field/scattered-field (TF/SF) region. A frequency domain monitor ‘flux_monitor’ is used to record the flux through the surface of the TF/SF box.
该脚本启用了一个沿 z 轴传播且偏振方向对应于约 26.5 度偏振角的平面波源。选择此角度是为了打破任何明显的对称性,并允许与所有模式耦合。平面波通过矩形总场/散射场(TF/SF)区域注入。使用频域监视器“flux_monitor”来记录通过 TF/SF 箱表面的通量。
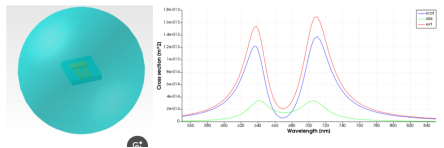
After the simulation is finished, the 'sigma_front' flux result corresponds to the scattering cross-section and the 'sigma_back' to the absorption cross-section. The sum of scattering and absorption cross section is the extinction cross section. The script will automatically plot all three cross sections as shown below
模拟完成后,“sigma_front”通量结果对应散射截面,“sigma_back”对应吸收截面。散射截面和吸收截面之和即为消光截面。脚本将自动绘制所有三个截面,如下所示。